The Pmax of a substance is the maximum pressure that is monitored during ignition of substances at different concentrations in a laboratory test facility. Tests are performed according to EN 13673-1 : “Determination of the maximum explosion pressure and maximum rate of pressure rise of gases and vapours – Part 1: Determination of the maximum explosion pressure”.
The graph shows a typical situation for methane (CH4). Methane has a Lower Explosion Limit of 4,4 vol% and an Upper Explosion Limit of 17 vol%. The graph shows us that an ignition of a concentration just above the LEL of 4,4 vol% will lead to pressure rise but, but not directly to a Pmax value. The optimum concentration for a complete combustion of the flammable substance and oxygen is appr. 10,8 vol%. At that concentration the maximum pressure rise is detected.
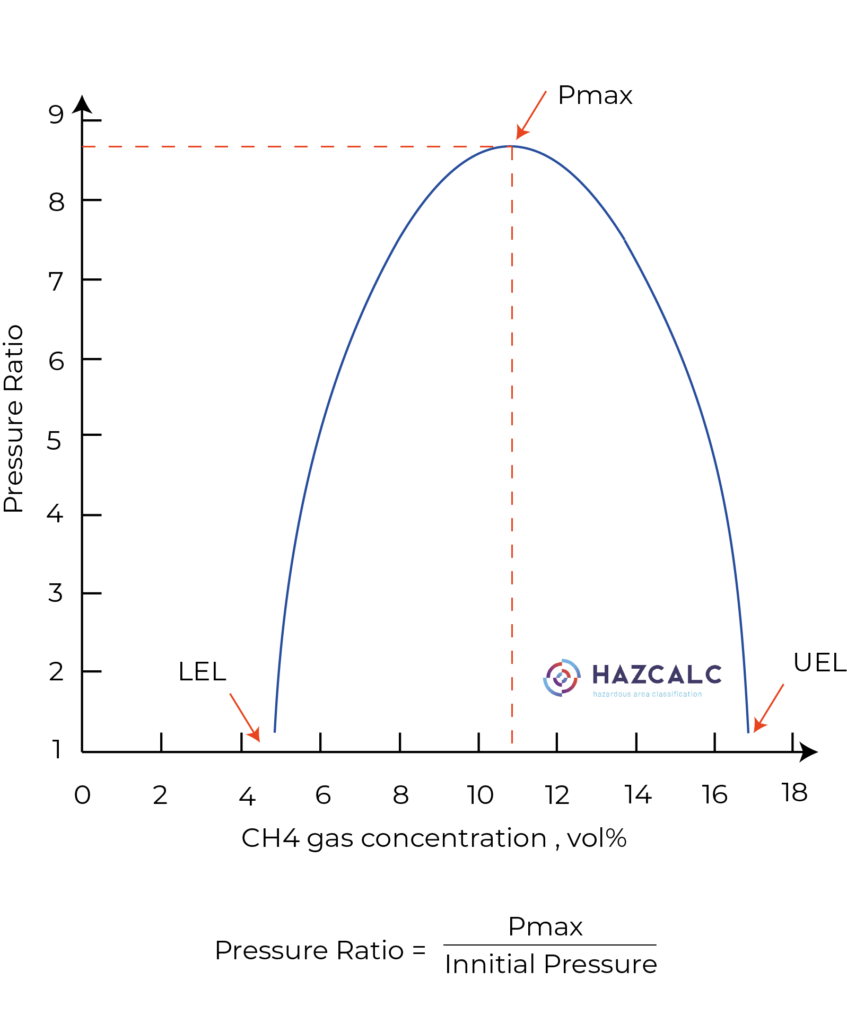
The Pmax is used for assessing the consequences of an explosion and determination of additional safety measures like explosion relief venting and the calculating the strength of explosion resistant equipment.